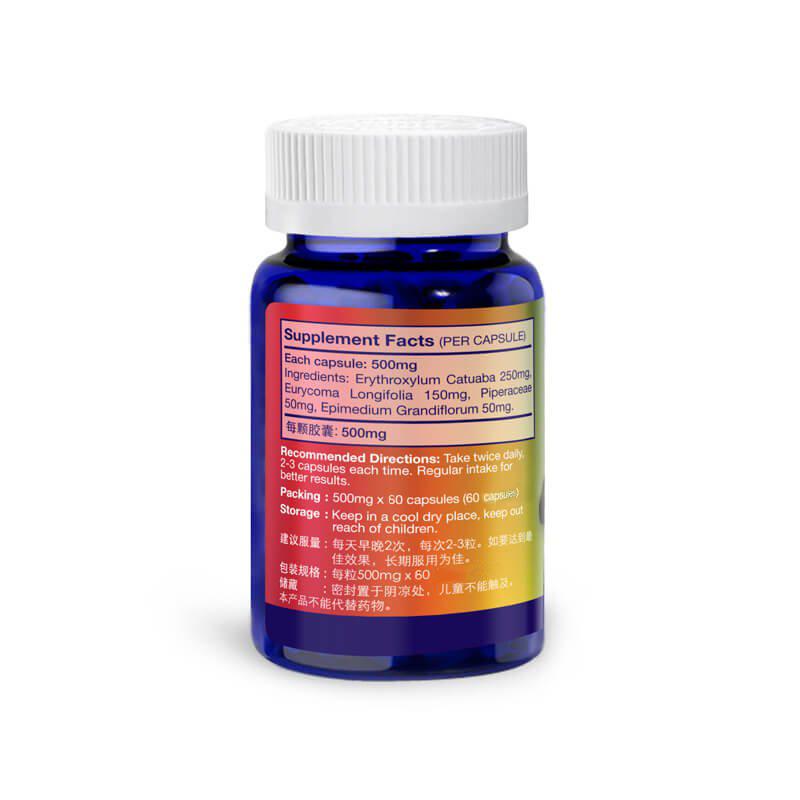
Our blog offers in-depth resources on men's sexual health, with a special focus on the most searched concerns like
erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, penis enlargement, and the use of natural sex pills. We cover trending
ingredients such as tongkat ali and cistanche, often included in herbal supplements for libido and erection support.
Readers will find trusted information on how to treat erectile dysfunction naturally, how to last longer during sex,
and what sex pills for men really work without harmful side effects. We also explore safe methods for penis
enlargement, comparing pills, pumps, extenders, and topical oils.
Posts include reviews of the best natural male enhancement products, alternatives to ED medications like Viagra, and
tips to improve sexual stamina and confidence. You'll learn whether penis pumps are effective, how tongkat ali
works, and how to choose the right solution for your needs.
Whether you're exploring penis growth methods, looking for natural ways to treat ED, or researching cures for
premature ejaculation, our blog provides comprehensive, evidence-based content to help men take control of their
sexual wellness.
Everything you need to know about Piperaceae Family
Welcome to our blog dedicated to the wonders of the Piperaceae family, a group of plants celebrated for their unique properties and extensive uses in natural herb supplements. If you’re passionate about natural health, the piper plant and its relatives, including the amazing long pepper, are essential to know. Let’s explore the fascinating world of the Piperaceae and uncover why these plants are treasured across cultures and continents.
Understanding the Piperaceae Family
The Piperaceae family, commonly known as the pepper family, includes over 3,600 species of flowering plants across 13 genera. This diverse group comprises some of the most well-known and widely used plants in herbal medicine and cuisine. Among the notable members are Piper nigrum (black pepper), Piper methysticum (kava), Peperomia pellucida, and Piper longum (long pepper).
The Versatile Piper Genus
The Piper genus is one of the most significant within the Piperaceae family. It includes several species that have been vital in global spice trade and traditional medicine for centuries. The active compounds in these plants, such as piperine found in black pepper and long pepper, are celebrated for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
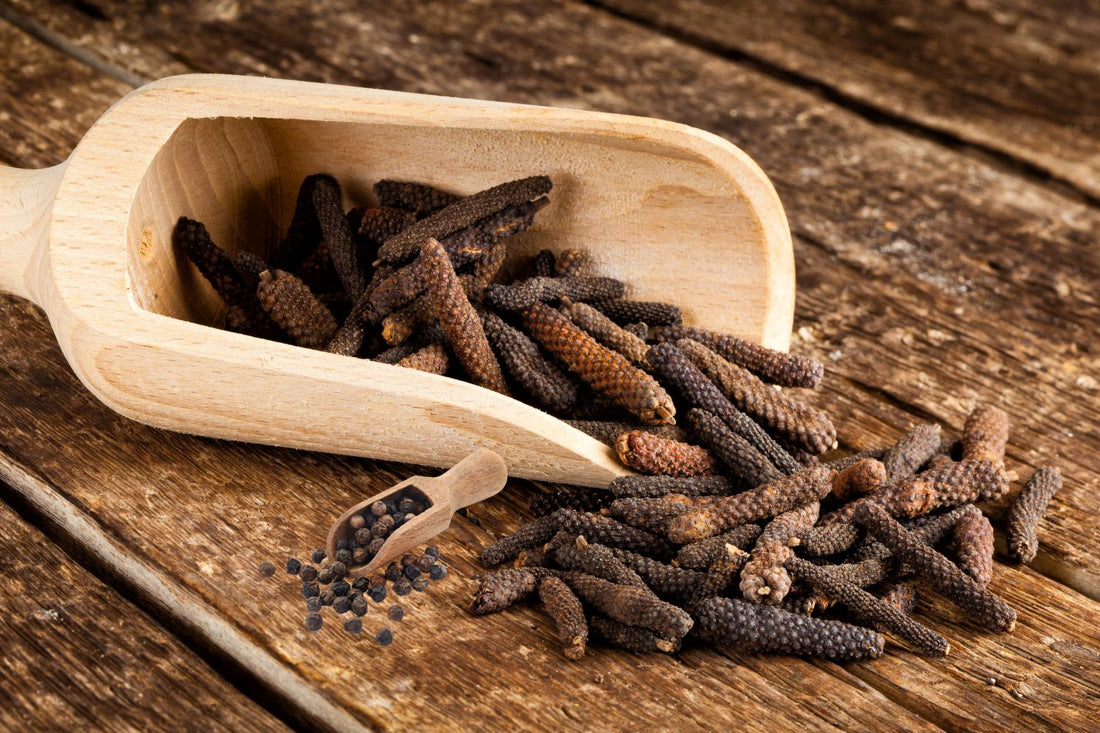
Long Pepper: A Hidden Gem in the Piperaceae Family
Piper longum, commonly known as long pepper, is a notable member of the Piperaceae plant family. This spice has a rich history in Ayurvedic and traditional Chinese medicine. Long pepper is known for its potential health benefits, including enhancing digestion, reducing inflammation, and supporting respiratory health. Its unique, pungent flavor also makes it a valuable addition to various culinary dishes.
Peperomia Pellucida: Another Treasure of the Piperaceae Family
Peperomia pellucida is another valuable member of the Piperaceae plant family. Often referred to by its common name, "shiny bush," this plant is used in traditional medicine to treat ailments such as arthritis and skin conditions. Its widespread use in tropical regions highlights its importance as a Piperaceae common name plant utilized for health benefits.
Health Benefits of Piperaceae Plants
Plants within the Piperaceae family are valued not only for their culinary uses but also for their medicinal properties. These plants are rich in essential oils, alkaloids, and other bioactive compounds that contribute to their therapeutic effects. For instance:
-
Piper longum (Long Pepper): Known for its digestive and anti-inflammatory benefits.
-
Piper nigrum (Black Pepper): Recognized for its antioxidant properties.
-
Piper methysticum (Kava): Used for its calming effects and as a natural remedy for anxiety.
-
Peperomia pellucida: Celebrated for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties.
The Beauty of Piperaceae Flowers
The Piperaceae flowers may not be the most conspicuous in the plant kingdom, but they play a crucial role in the reproductive cycle of these plants. Typically small and greenish, these flowers are adapted to specific pollinators, contributing to the diversity and survival of the Piperaceae plants.
Conclusion
The Piperaceae family plants are remarkable for their rich history and promising future in natural health and wellness. Whether you are looking to enhance your diet with the robust flavor of long pepper or seeking natural remedies like Peperomia pellucida for its medicinal properties, the Piperaceae has something valuable to offer.
Explore our range of natural herb supplements containing Piper longum and other members of the Piperaceae plant family. Experience the health benefits that nature has bestowed upon these extraordinary plants. Embrace the power of the pepper family and let the Piperaceae enrich your journey to wellness.
Reference
- Mabberley, D.J. (2008). Mabberley's Plant-Book: A Portable Dictionary of Plants, their Classifications, and Uses. Cambridge University Press.
- Quattrocchi, U. (2012). CRC World Dictionary of Medicinal and Poisonous Plants. CRC Press.
- Chopra, R.N., Nayar, S.L., Chopra, I.C. (1956). Glossary of Indian Medicinal Plants. Council of Scientific and Industrial Research.
- Srinivasan, K. (2007). Black pepper and its pungent principle-piperine: A review of diverse physiological effects. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 47(8), 735-748.
- Wiart, C. (2006). Medicinal Plants of Asia and the Pacific. CRC Press.
- Oliveira, F.Q., Andrade-Neto, M., Krettli, A.U., Brandao, M.G.L. (2004). New evidences of antimalarial activity of Piperaceae products. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia, 14(2), 1-6.
- Jaramillo, M.A., Manos, P.S. (2001). Phylogeny and patterns of floral diversity in the genus Piper (Piperaceae). American Journal of Botany, 88(4), 706-716.
- Yuncker, T.G. (1970). The Piperaceae of Brazil. II. Flora Neotropica, 2(3), 1-206.
- Muñoz, J. (2004). Piperaceae: The Pepper Family. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
- Martínez, M., Díaz, R. (2001). Ethnobotany of the Piperaceae Family in Mexico. Economic Botany, 55(4), 547-553.